- +91 - 9101168739
- hello@drkanchanmurarka.com
- Guwahati, Assam
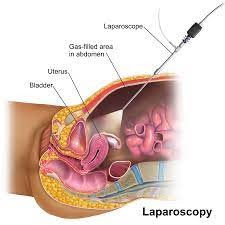
Laparoscopy is a surgical diagnostic procedure used to examine the organs inside the abdomen. It’s a low-risk, minimally invasive procedure that requires only small incisions.
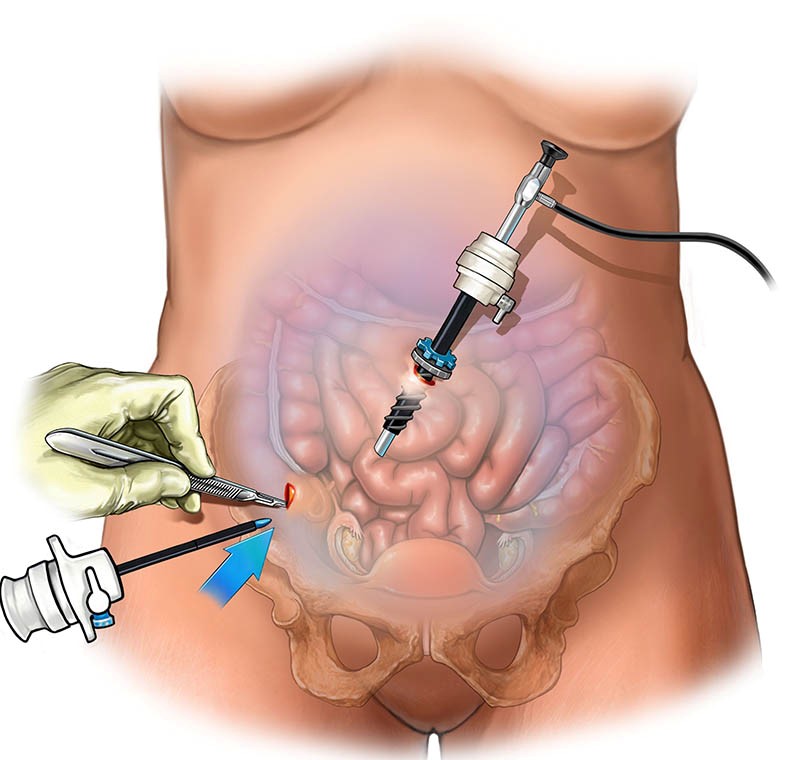
Laparoscopy uses an instrument called a laparoscope to look at the abdominal organs. A laparoscope is a long, thin tube with a high-intensity light and a high-resolution camera at the front. The instrument is inserted through a very small incision in the abdominal wall. As it moves along, the camera sends images to a video monitor and the surgeon does the operative procedure. It is a less invasive procedure in which women has less pain, less blood loss and can return to normal activity more quickly.
Laparoscopy can be used to identify and diagnose the pelvic pathologies. The treatment can also be done at the same time.
It can be used for diagnostic purposes where the scope is inserted into the abdomen and we look and identify the problems. Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed when noninvasive methods like ultrasound and hysterosalpingography are unable to provide enough information or insight for a diagnosis. The procedure may also be used to take a biopsy, or sample of tissue, from a particular organ. In patients with infertility it is usually performed to see the condition of pelvic cavity and tubes. It helps in diagnosing the cause of infertility like endometriosis , blocked and unhealthy tubes which may be missed by other diagnostic procedures.
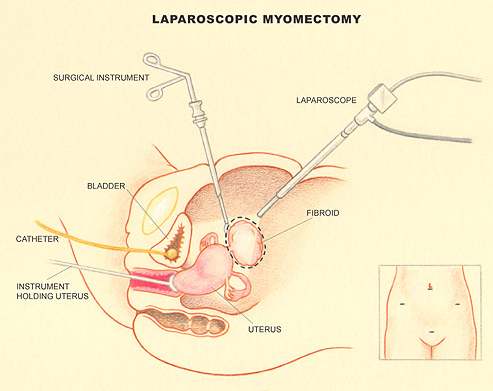
Laparoscopic Myomectomy is a surgical procedure of removing fibroids through small abdominal incisions. Laparoscopic Myomectomy is suggested and advised for those who experience problems due to fibroids like pelvic pain or pressure, heavy menstrual bleeding, urinary frequency, or infertility. This procedure is done when the woman wants to preserve the uterus but remove the fibroids.
Laparoscopic myomectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the fibroid. A small incision is made in the belly button and a tiny camera is inserted. The surgeon watches the image from this camera on a TV screen and performs the operative procedure. The myoma is shelled out from the uterus and taken out from abdomen in small pieces. It is a less invasive procedure in which women has less pain, less blood loss and can return to normal activity more quickly.
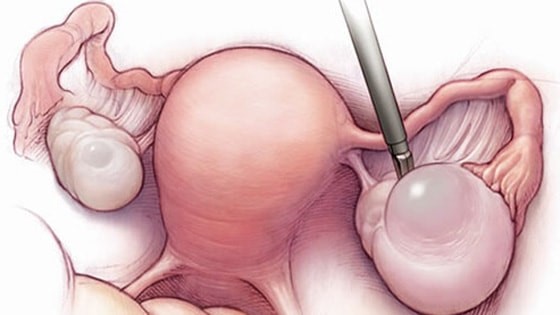
Laparoscopic cystectomy is the removal of ovarian cysts, or masses, using laparoscopy, a form of minimally invasive surgery. Laparoscopic cystectomy is used to remove cysts and growths on the ovaries that are persistent, enlarging or causing symptoms.
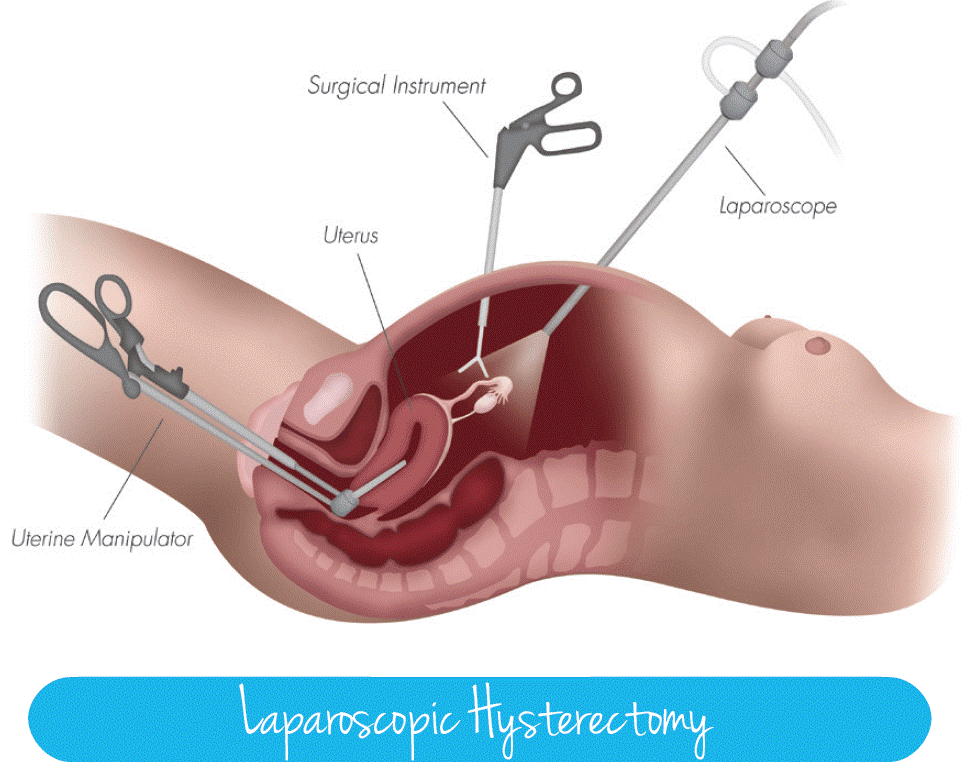
A laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the uterus. A small incision is made in the belly button and a tiny camera is inserted. The surgeon watches the image from this camera on a TV screen and performs the operative procedure.
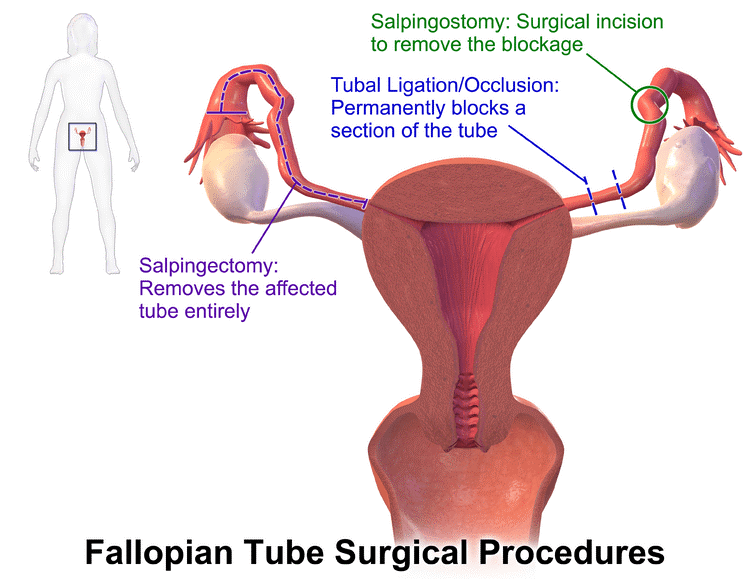
A Laparoscopic Salpingectomy is surgery to remove one or both fallopian tubes. Laparoscopic salpingectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure done to remove the tubes. It is done in patients whose tubes are diseased or if there is presence of hydrosalpinx ( presence of fluid inside the tubes). Hydrosalpinx decreases the chances of pregnancy and after removal of one tube the patient can conceive naturally. If both tubes are removed then the patient can conceive with the help of IVF (test tube baby).
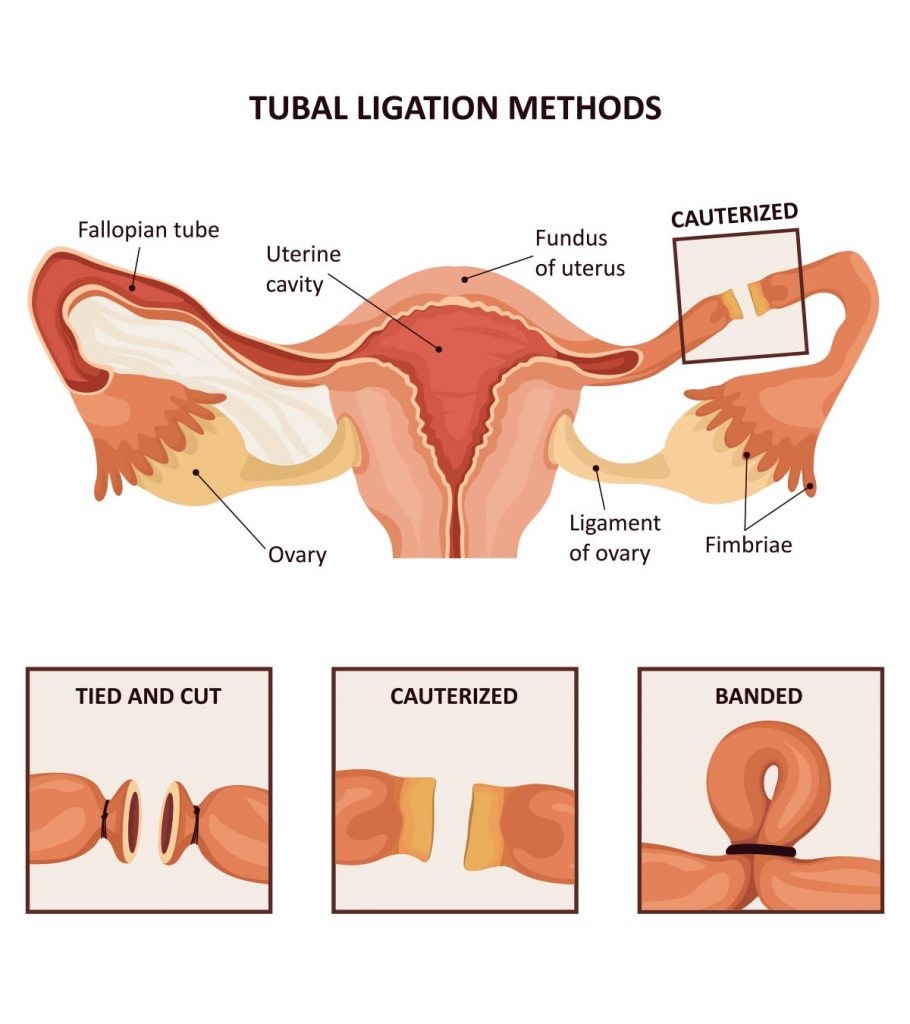
A tubal ligation is considered a permanent method of birth control. The fallopian tubes are cut or blocked, which prevents pregnancy by blocking the egg’s path to the sperm and uterus. Laparoscopy makes it possible to see and do the surgery through small incisions in the abdomen.
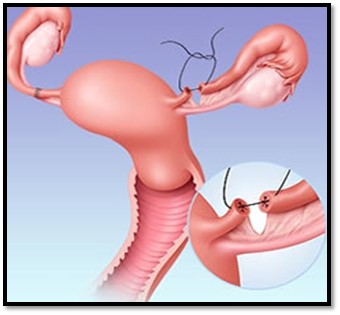
Laparoscopic tubal reanastomosis is a minimally invasive surgical procedure. It is usually done in patients who had undergone tubal ligation in the past but now again wants to conceive naturally. Laparoscopic tubal reanastomosis has the advantages of fewer complications, less postoperative discomfort, a smaller incisional scar, a shorter recovery time, and earlier resumption of normal activities. This technique has a satisfactory pregnancy rate in selected patients who desire reversal of tubal sterilization.